Each maxilla forms joints with seven other facial bones plus two of the cranium.
Keystone of the cranial floor.
Lies at the middle part of the base of the skull and is called the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones holding them all together.
Medical professionals often perceive the keystone of the cranial floor as off balance or restricted in its movement.
A prominent irregular wedge shaped bone at the base of the skull.
It is the keystone because it anchors all facial bones except the mandible.
The cerebrum cerebellum brainstem and orbits.
The function of the skull is both structurally supportive and protective 2.
This facial bone articulates with teeth.
The sphenoid bone has been called the keystone of the cranial floor since it is in contact with all of the other cranial bones the greek physician galen wrote that the sphenoid bone was like a.
When the structure deep inside the skull is not moving freely there can be many repercussions.
The sphenoid bone has been called the keystone of the cranial floor because it is in contact with all of the other cranial bones.
Sella turcica of the.
From a superior vantage point you can really see how it is central in its location and holds the surrounding cranial bones in place.
These cranial bones contain the organs of hearing and balance and articulate with the mandible.
A e b b c g d h e i answer.
As a direct or indirect result of hindered csf flow an inhibited sphenoid bone can cause many conditions.
Bones in the following area protect the brain.
Medium study objective 1.
It is frequently referred to as the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones and holds them together.
What bony depression of the cranial floor does the pituitary sit.
So 7 4 4 identify the location and surface features of the parietal bones.
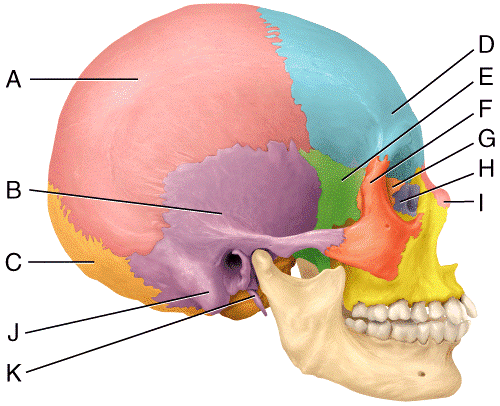
In the diagram which bone is considered the keystone of the cranial floor.
Posterior slightly superior to nasal cavity anterior view frontal plane superior view transverse plane lateral view sagittal plane.
43 in the diagram which bone is considered the keystone of the cranial floor.
It protects its inner contents.
So 7 4 describe the cranial and facial bones and their main features.
The sphenoid bone is the keystone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones.
These bones are the nasal zygomatic lacrimal inferior nasal concha palatine vomer the adjacent fused maxilla frontal ethmoid.